Discover how Persia's rich cultural heritage, from the philosophy of Avicenna to the poetic brilliance of Rumi, profoundly shaped Islamic civilization.
Delve into the architectural marvels, administrative innovations, and artistic traditions that forged a lasting interplay between Persian and Islamic cultures.
Persian Philosophical Contributions
Persian philosophers like Avicenna and Al-Farabi profoundly influenced Islamic thought by integrating Greek, Persian, and Islamic traditions into a cohesive philosophical framework. By emphasizing reason, ethics, and metaphysics, they laid the groundwork for what would become a rich and enduring Islamic philosophy.
Avicenna's 'The Book of Healing' is a prime example, delving into various branches of knowledge and deeply impacting Islamic intellectual traditions.
Avicenna and Al-Farabi were instrumental in shaping concepts of unity, existence, and reality. Their works explored the nature of being and the structure of the cosmos, providing a foundation for Islamic metaphysical discourse.
Their philosophical contributions went beyond metaphysics to address ethics, politics, and theology, offering a thorough approach to understanding human existence and governance.
In particular, Al-Farabi's political philosophy sought to harmonize rational governance with Islamic teachings, influencing subsequent Islamic political thought.
These philosophers didn't merely translate Greek works; they synthesized them with Persian and Islamic ideas, creating a unique philosophical system.
Understanding their contributions helps you appreciate how Persian philosophy shaped the intellectual and spiritual development of Islamic civilization, making it a cornerstone of Islamic scholarly traditions.
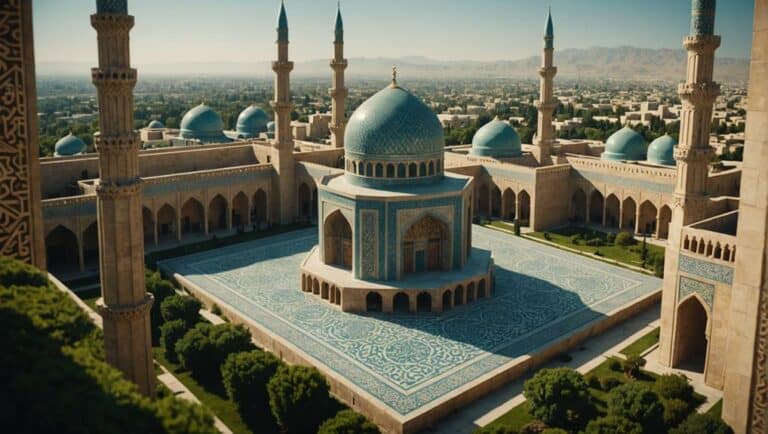
Architectural Innovations
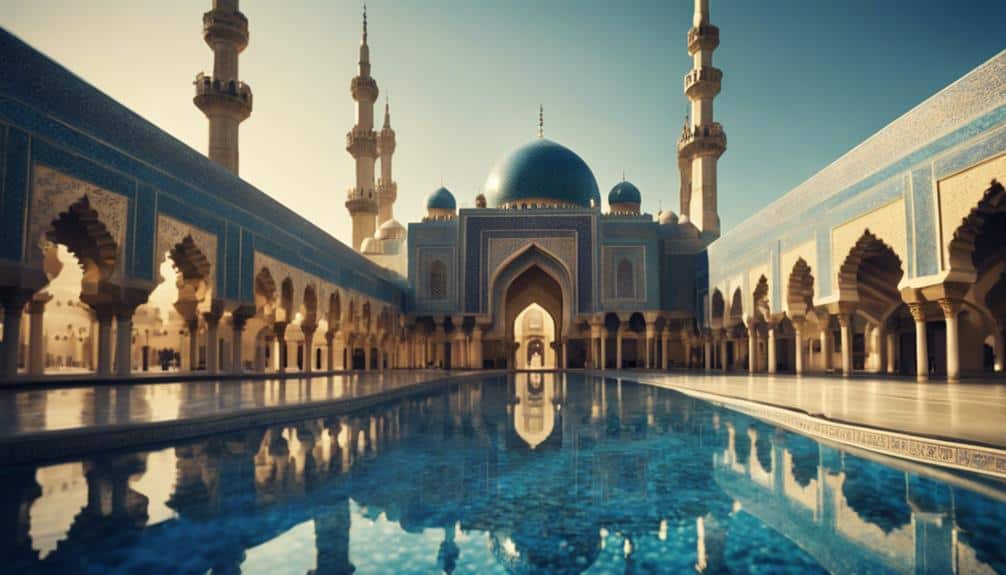

When examining Persian architectural innovations, you'll notice the transformative impact of structural elements like the Iwan and the Charbagh garden layout.
Persian artistic design techniques, including intricate tile work and arabesques, have seamlessly integrated into Islamic architecture.
This fusion hasn't only enhanced aesthetic appeal but also influenced iconic structures such as the Taj Mahal and Alhambra.
Persian Structural Elements
The architectural innovations from ancient Persia, such as the Iwan and Charbagh garden layout, have profoundly influenced Islamic civilization's aesthetic and structural designs. Persian art and architecture introduced these elements with an emphasis on grandeur and symmetry, which became integral to Islamic art and architecture.
The Iwan, a vaulted hall or space, open on one side, exemplifies Persian aesthetics that highlight both functionality and beauty. This structure has been adopted widely in Islamic buildings, serving as a monumental entrance or a congregational hall.
The Charbagh garden layout, another Persian innovation, incorporates quadrilateral garden designs divided by walkways or flowing water, symbolizing paradise. This layout has been pivotal in shaping the aesthetic frameworks of Islamic gardens, seen in iconic structures like the Taj Mahal.
Persian architecture's influence extends to the intricate tile work, arabesques, and calligraphy that adorn many Islamic buildings, reflecting a deep intertwining of artistic and architectural practices.
Artistic Design Techniques
Drawing from ancient Persia's architectural heritage, Islamic civilization adopted and adapted innovative design techniques that melded functionality with aesthetic grandeur. Persian design elements like the Iwan, a large vaulted hall, and the Charbagh garden layout, with its quadrilateral design symbolizing paradise, became integral to Islamic architectural legacy. The pishtaq, a rectangular frame around an arched opening, also influenced iconic Islamic structures.
You can see the impact of Persian aesthetics in the intricate tile work, arabesques, and calligraphy that adorn mosques and palaces. These elements don't just serve decorative purposes; they reflect deep spiritual and poetic narratives. Geometric patterns, a hallmark of Persian design, became central to Islamic art, symbolizing the infinite nature of creation and the unity of God.
Iconic structures like the Taj Mahal and the Alhambra in Spain are prime examples of how Persian design techniques fused with Islamic traditions to create timeless masterpieces. The use of calligraphy, often featuring verses from the Quran, complements the geometric patterns and arabesques, offering both visual and intellectual engagement.
This fusion of Persian and Islamic design techniques has left an indelible mark on the architectural legacy of Islamic civilization.
Literary and Artistic Impact
When you examine the literary and artistic impact of Persia on Islamic civilization, you'll see how Persian poetry, particularly the works of Rumi and Hafez, established enduring legacies in Islamic literature.
Persian calligraphy and miniature painting techniques fostered a fusion of artistic traditions, leading to innovative expressions within the Islamic world.
Additionally, the Shahnameh by Ferdowsi not only preserved pre-Islamic Persian mythology but also influenced subsequent Islamic literary and artistic works.
Persian Poetry's Enduring Legacy
Persian poetry, epitomized by figures like Rumi and Hafez, profoundly influences Islamic literary traditions through its innovative forms and timeless themes.
By exploring Persian poetry, you'll discover its pivotal role in shaping Islamic poetry, particularly through the adoption of poetic forms such as the ghazal and qasida. These forms have set enduring standards, showcasing the intricate blend of emotion and intellect.
To appreciate Persian poetry's enduring legacy, consider these key points:
- Innovative Forms: Persian poets like Rumi and Hafez masterfully crafted the ghazal and qasida, enriching Islamic poetry with new expressive possibilities.
- Timeless Themes: Themes of love, mysticism, and spirituality in Persian poetry resonate deeply within Islamic cultures, transcending time and geography.
- Calligraphic Art: The calligraphy of Persian poetry, often adorning mosques and monuments, creates a harmonious blend of literary and visual art, enhancing spiritual experiences.
- Global Influence: Persian poetic works are celebrated and studied worldwide, attesting to their universal appeal and depth.
Artistic Fusion and Innovation
By intertwining Persian literary traditions with Islamic aesthetics, a unique cultural synthesis emerged, showcasing both innovation and continuity. Persian influence on Islamic art is evident in the intricate calligraphy, geometric patterns, and poetic narratives that grace architectural marvels.
The Shahnameh, a cornerstone of Persian literature, not only enriched Islamic literary traditions but also infused architectural designs with its epic tales and elaborate motifs.
The artistic fusion of Persian aesthetics within Islamic art led to the creation of stunning tile work, arabesques, and ornate decorations that define Islamic architecture. You see this in iconic structures like the Taj Mahal and the Alhambra, where Persian-inspired elements blend seamlessly with Islamic principles, reflecting a rich cultural legacy.
This fusion also extended to visual arts, where Persian miniatures influenced manuscript illumination, and Persian gardens inspired Islamic landscaping. This synthesis of artistic elements showcased a blend of tradition and innovation, ensuring the continuity of Persian influence within Islamic civilization.
Ultimately, the cultural legacy of Persian aesthetics within Islamic art represents a profound symbiosis, one that has left an indelible mark on the artistic heritage of the Islamic world, fostering a legacy that continues to inspire and captivate.
Administrative Systems

Islamic governance structures were profoundly shaped by the sophisticated administrative systems of ancient Persia, including the Divan and Diwan. These Persian administrative systems introduced a level of bureaucratic organization that Islamic caliphates adopted and refined. The Divan, a central bureau for managing state affairs, and the Diwan, which handled financial records, became integral components of Islamic administration, guaranteeing efficient governance.
The role of the Vizier, derived from Persian practices, emerged as a high-ranking official responsible for overseeing these bureaucratic functions. This position was pivotal in maintaining the stability and efficiency of Islamic governance. Persian influence can be seen in several aspects of Islamic administrative systems:
- Meritocratic Principles: Emphasizing merit and competence in bureaucratic appointments.
- Centralization: Streamlining authority to secure effective control over vast territories.
- Efficient Taxation: Developing sophisticated taxation systems to support the state financially.
- Record-Keeping: Adopting meticulous record-keeping methods for accountability and transparency.
These elements combined to create an administrative framework that allowed Islamic civilizations to thrive. By adopting Persian principles, Islamic states not only borrowed effective governance techniques but also guaranteed the longevity and stability of their rule.
This integration highlights the enduring legacy of Persian administrative genius in shaping Islamic civilization.
Religious and Spiritual Influence
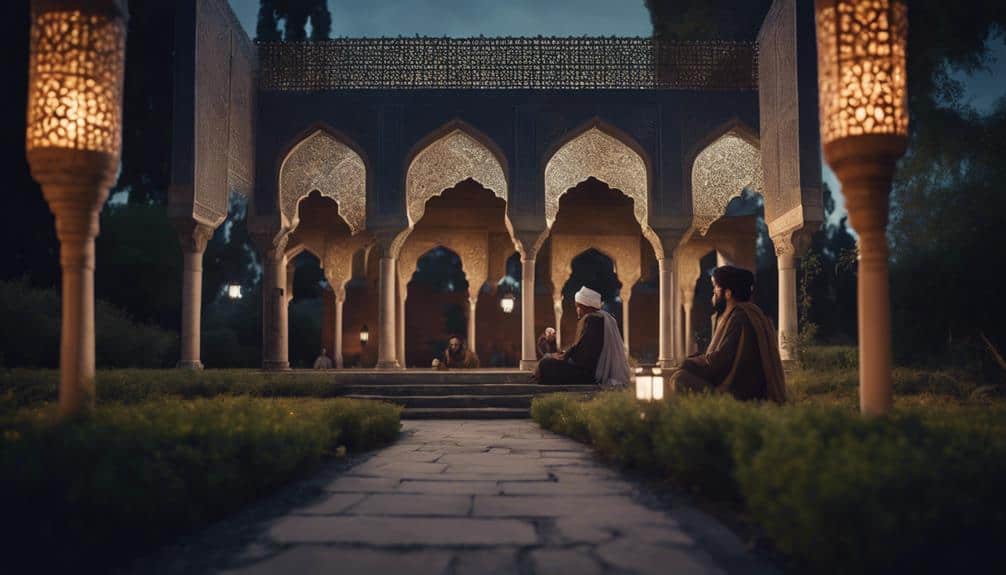

The profound interplay between Persian religious thought and Islamic theology catalyzed a synthesis that enriched Islamic beliefs and practices. By integrating elements from Zoroastrianism, Manichaeism, and other pre-Islamic traditions, Persian scholars contributed to a deeper, more nuanced understanding of Islamic theology. This fusion is evident in the philosophical works of figures like Al-Farabi and Avicenna, whose writings reflect a melding of Greek philosophy, Islamic theology, and Persian intellectual traditions.
Persian languages also played a pivotal role in the development of Islamic literature and poetry. The Persian language became a medium through which complex theological and philosophical ideas were expressed, influencing the literary style of Islamic texts. This influence extended to Islamic art, where Persian aesthetics—characterized by intricate geometric patterns and exquisite calligraphy—became defining features of Islamic artistic expression.
In addition, Islamic jurisprudence was shaped by Persian administrative systems and legal practices. The integration of these systems facilitated the development of a cohesive legal framework that governed diverse Muslim communities.
Therefore, the Persian influence permeated various aspects of Islamic civilization, creating a rich cultural tapestry that continues to impact contemporary Islamic societies.
Fusion in Daily Life
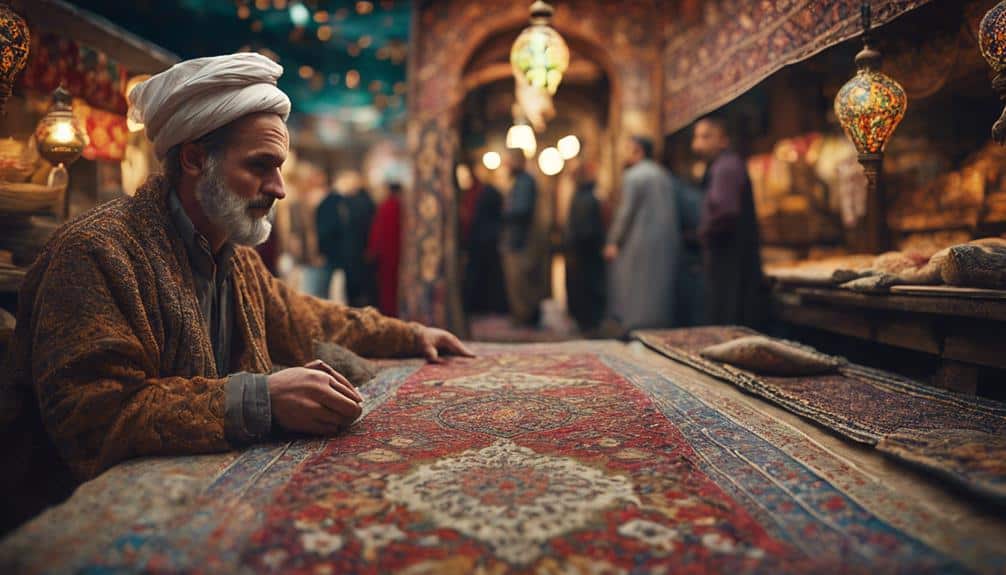

You can observe the profound Persian influence in Islamic daily life through the seamless integration of Persian art, architecture, and cultural practices into everyday rituals and expressions. This fusion is evident in various aspects of life that have been enriched by Persian contributions.
- Persian Calligraphy and Poetry: The elegant strokes of Persian calligraphy and the evocative verses of Persian poetry have become central to Islamic artistic expression, decorating mosques and manuscripts.
- Architectural Elements: Persian-inspired architectural designs, such as the use of iwans (vaulted spaces) and intricate tile work, are hallmarks of many Islamic structures, creating spaces that inspire awe and reverence.
- Culinary Traditions: The inclusion of Persian culinary traditions, like flavorful kebabs and aromatic rice dishes, highlights the blending of tastes and techniques that characterize Islamic cuisine.
- Music and Performance: Persian musical instruments and styles have been adopted and adapted, enriching the auditory landscape of Islamic cultures with their melodious and rhythmic complexities.
This fusion of Persian influence within Islamic daily life underscores the dynamic interplay between these two rich cultures. By incorporating Persian art and cultural practices, Islamic societies have cultivated a unique and vibrant cultural tapestry that continues to thrive and evolve.
Modern Reflections
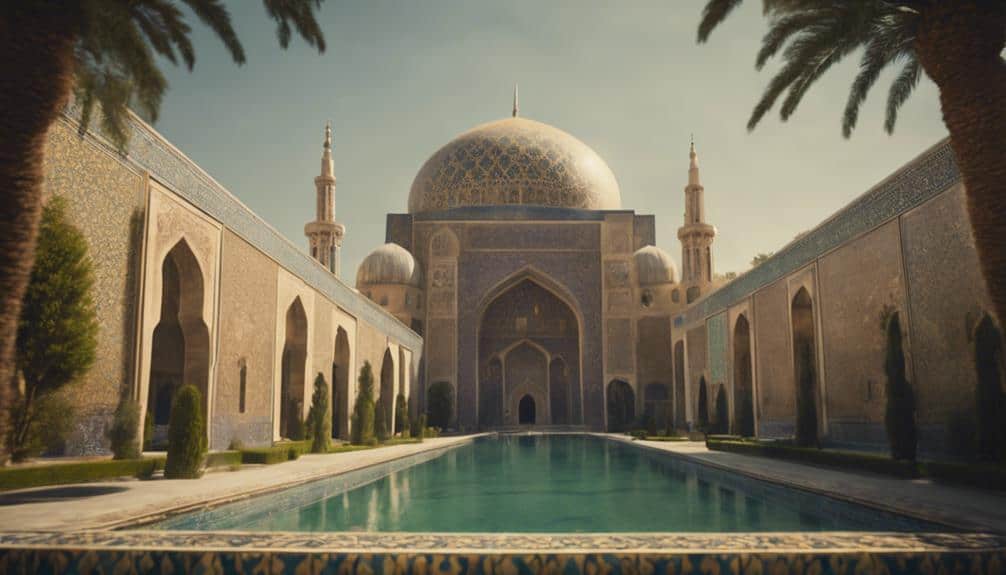

Modern reflections on Persian influence reveal a seamless integration of traditional Persian aesthetics into contemporary Islamic art and culture, highlighting the enduring legacy of this cultural symbiosis.
In modern architecture, you'll notice the prevalence of intricate tile work and arabesques, which are direct descendants of Persian design philosophies. These elements not only embellish buildings but also evoke a deep sense of historical continuity.
Contemporary artistic practices frequently draw from the rich tapestry of Persian rugs, textiles, and gardens. By incorporating these traditional patterns into modern designs, artists guarantee that Persian aesthetics remain relevant and vibrant. Persian-styled gardens, with their meticulous layout and symbolic motifs, continue to inspire various cultural expressions, underscoring their timeless beauty.
Persian poetry, with its profound themes and elegant styles, remains a significant influence on modern literary works. The resonance of its themes in contemporary artistic practices speaks volumes about its lasting appeal.
Similarly, Persian calligraphy, celebrated for its beauty and elegance, is widely admired in modern art. Its timelessness is evident in the way it continues to captivate and inspire, showcasing the perpetual relevance of Persian aesthetics in today's creative landscape.


